Introduction
Digital technology is creating an information-rich environment; people are constantly receiving data from multiple information sources (news media, social networks, email, mobile notifications, etc.). This access to information can be beneficial; however, when people consume too much information at once, the brain may become overstimulated and overwhelmed, leading to increased anxiety.
By constantly consuming information through social networks, reading negative articles, and scrolling through endless posts or tweets, a user remains in a heightened state of readiness and cannot unwind or concentrate on anything else.
Eventually, as they continue to consume large amounts of information, they will experience higher levels of stress, confusion, and anxiety, as well as the feeling that they cannot stop accumulating new information.
Therefore, comprehension of how these processes occur is critical for keeping emotions balanced. Understanding how to manage your information intake can help you lower your anxiety, enhance your ability to maintain focus, and protect your overall mental health.
Information Overload
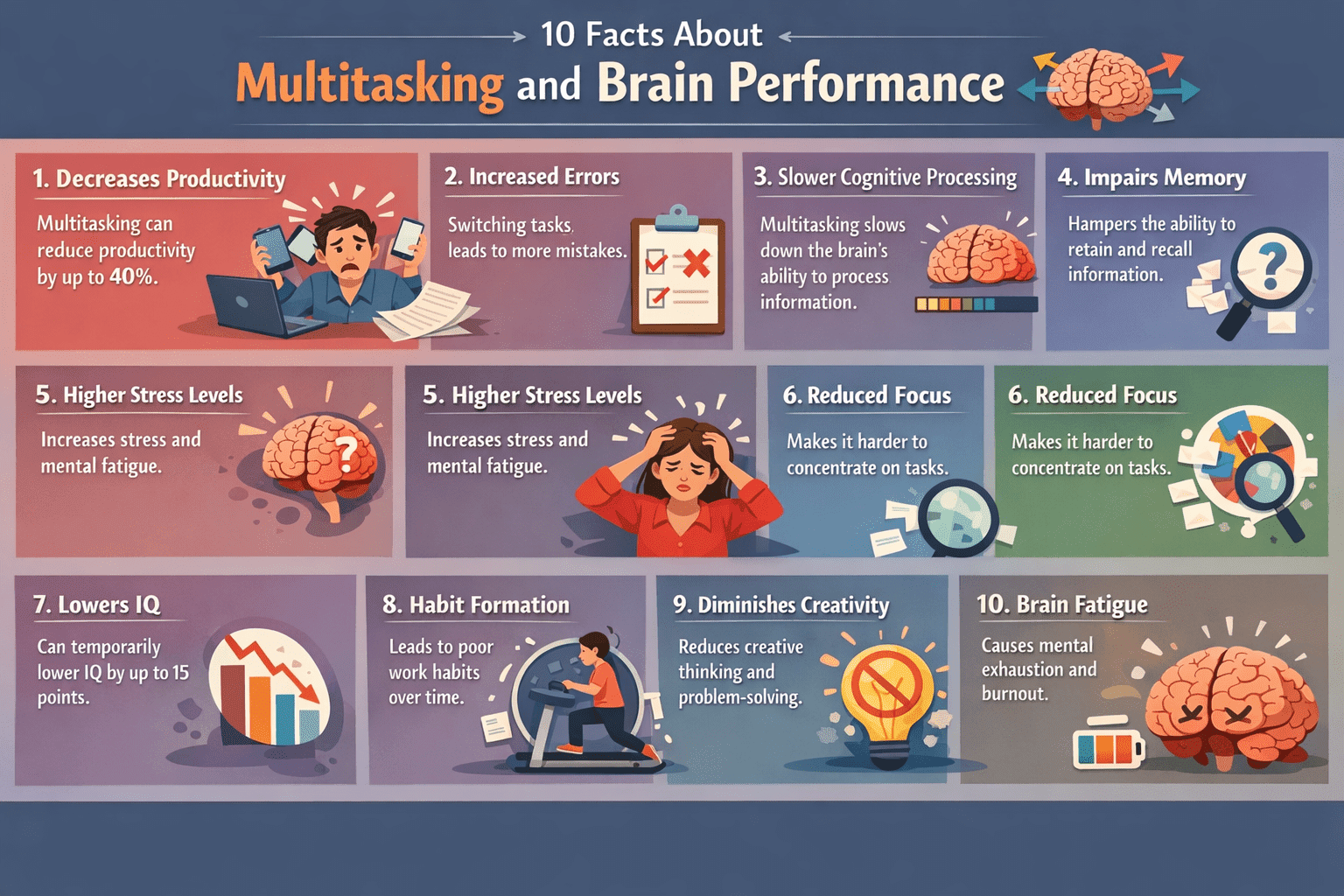
The term “Information Overload” describes a consequence of the constant flood of messages, digital content, and an overabundance of tasks from your phone or stream (Facebook, Twitter, text, etc.).
The overabundance of information can overwhelm individuals to where it limits their ability to understand and adequately respond, and ultimately results in mental fatigue, poor decisions, and reduced productivity.
Characteristics of an Information Overload
Excessive Amounts: Too much information in a short time.
Overly Complex: Information that is difficult to comprehend or synthesize.
Difficult to Process: Difficulty filtering, prioritizing, and making sense of the information that you receive.
Common symptoms of Information Overload
Analysis Paralysis: Difficulty making a decision because you have so many choices.
Reduced Productivity: Spent more time sorting through information than actually working.
Stress and Anxiety: With the constant stream of alerts, people often experience mental fatigue, feeling overwhelmed, and burnout.
Divided Attention: Difficulty focusing on a single message due to multiple streams of incoming information.
Lower Quality of Work: Because of the time that is lost to make decisions based on an incomplete understanding of the information, most decisions are hasty, and therefore more likely to make mistakes.
Social Media Impact
Findings from research studies indicate that social networking sites increase an individual’s level of social anxiety, which ultimately results in increased mental health issues.
Individuals are continuously subjected to many updates, opinions, memes, etc., that can overwhelm the individual.
The constant influx of notifications associated with “likes,” comments, etc., and trending topics may contribute to an individual feeling as if he/she is always “on alert,” and make it more challenging to unwind or disconnect from the social networking site.
When individuals compare themselves to others via social networking sites, there is a positive correlation between that comparison and self-doubt about oneself and anxiety due to the pressure to keep up with others.
Through the presence of negative news, arguments, and unrealistic portrayals of reality, one experiences emotional difficulties as a result of using social networking sites. Social networking sites are designed to attract attention and thus encourage users to use the site often and for long periods of time, contributing to mental fatigue.
Prolonged exposure to these sites can interfere with concentration, decrease sleep quality, and increase levels of anxiety over time. The idea of being “connected” or “informed” leads many individuals to feel the fear of missing something, or to be emotionally drained.
By understanding how social networking sites can negatively affect an individual’s mental health, the individual can be more mindful of his/her social networking usage. By reducing notifications, taking regular breaks from social networking, or limiting usage of social networking, individuals can decrease anxiety and improve their overall mental health.
Mental Saturation
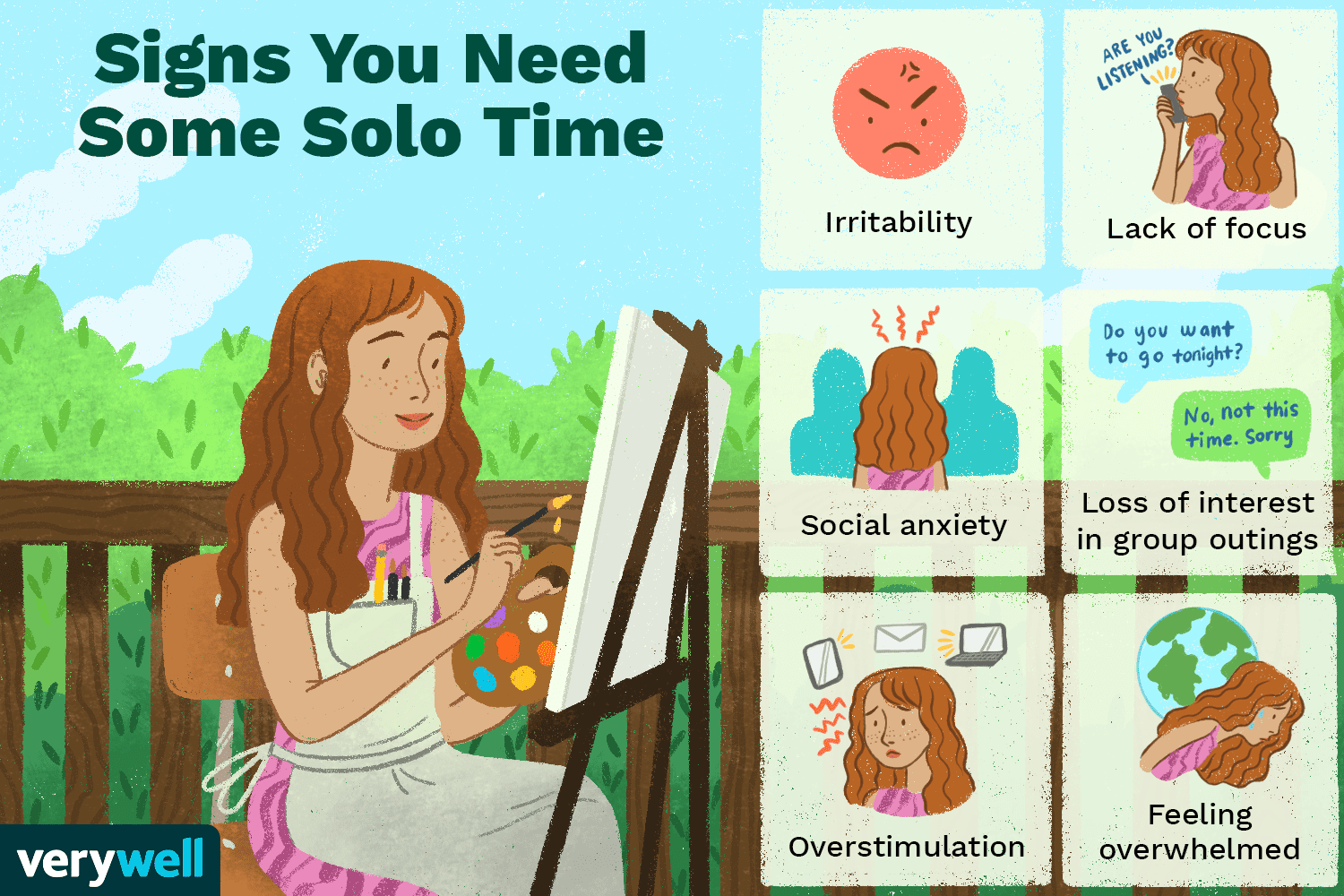
Mental saturation, or mental exhaustion/brain fog, is a sense of feeling overwhelmed, drained, and unable to think clearly as a result of mental stress for a long time, being overly focused on something, or experiencing lots of emotional stress, and presents itself with symptoms like poor concentration, irritability, lack of motivation, and apathy.
Unlike physical fatigue that can be corrected with sleep, mental saturation is the brain’s way of telling you it needs a break from all of the things it is required to do at once (multitasking), in high pressure jobs (where success equals money, supervisor approval etc.), and during caregiving. Ignoringmental saturation can lead to chronic burnout.
Signs/Symptoms
Cognitive – Brain fog, poor focus, memory problems, difficulty making decisions, inability to complete tasks.
Emotional – Mood swings, irritability, feeling anxious, apathetic, hopeless or detached from oneself, negative thoughts.
Behavioural – Zoning out (not being present), inability to concentrate, getting distracted easily, snapping at others, lack of interest in hobbies.
Overload- Engaging in constant multitasking, being employed in a high pressure work environment, and dealing with multiple family crisis situations or caring for a family member who is chronically ill.
Physical (Related)- Sleeping problems, fatigue, headache, muscle pain, appetite changes, etc.
Causes
Stress- Experiencing a lot of stress for an extended period of time or from situations such as chronic stress, anxiety, grief, or being emotionally drained or experiencing financial problems.
Lifestyle- A lack of sleep, poor nutrition, and prolonged, intense focus on one task/interest/hobby.
Filtering Content
Content filtering helps eliminate some of the anxiety that comes with consuming too much information by determining ahead of time what type of information we want to consume, and limiting how much of the other types of information we are exposed to.
For instance, by unsubscribing from accounts that post content we do not want to see or find helpful, muting too many notifications, following only credible news sources, and turning off notifications for all but the most important news, people are able to filter out much of the excess mental clutter that catches our attention.
Filtering content is a tool for getting your brain to stay focused on the things that are really important, instead of being bombarded with 24/7 updates and opinions, and for preventing the sense of emotional exhaustion that arises from repetitively viewing distressing or inconsistent information.
People who establish times during the day to view news and social media will be able to better manage their intake of information and will likely be less prone to compulsively check their social media feeds and email accounts.
By having a purposeful strategy for filtering what type of information you receive on a daily basis, filtering content can allow you to have less anxiety and more time and energy to devote to your day-to-day activities. You will be informed about the world around you and will not likely feel overwhelmed or stressed out.
Filtering content will also foster healthier digital behaviors, lower levels of anxiety and help improve focus and maintain emotional balance. By filtering content on a regular basis, you will be able to maintain a clear mind, better protect your mental health and maintain a calmer, more focused state of mind in today’s increasingly information-saturated world.
Healthy Consumption
Healthy information consumption means accessing and consuming information purposefully and in a balanced way instead of mindlessly reading everything there is about a topic. Healthy information consumption means that quality of information is more important than quantity and, therefore, provides enough time for a person’s brain to process and understand the information without feeling stressed.
When a person uses healthy information consumption, they will have established healthy boundaries with their screen time, chosen reputable sources of information, and avoided unnecessarily subjecting themselves to negative or sensational information that creates a sense of distress.
They will also have taken time away from the news/social media and allowed their brain a chance to rest and recover. Setting aside certain times in the day to check for updates will also help eliminate excessive scrolling and subsequently, lower the amount of stress on the person.
An individual can achieve emotional balance and mental clarity by connecting their digital life to their offline life through exercise, reading, dedicated hobbies, and spending time in nature. Listening to the limits of one’s mental health is critical in promoting and achieving healthy information consumption; if an individual feels overwhelmingly anxious, they should remove themselves from consuming information at that moment.
Practicing healthy information consumption will improve a person’s focus, anxiety levels, and overall mental health. Results illustrate that continuous practicing of healthy information consumption helps an individual remain informed while maintaining their calmness, productivity, and emotional stability.
Conclusion
The following reasons contribute to the anxiety caused by the continual influx of information:
Because our brains cannot effectively handle the sheer volume and complexity of information being presented to us, they become overburdened with all of the information they receive.
This leads to cognitive overload, fatigue, and a constant feeling that something is constantly going on and we don’t know what it is or if it may be harmful or threatening to us.
Because the majority of the information we receive is about events that are negative or troubling, this has a tendency to keep us engaged in the “fight or flight” reflex (hyper-arousal). Therefore, when we read or watch the news, read social media posts, and view other media that consists of a lot of negative information, this activates our fight or flight reflex and keeps us physically and emotionally aroused.
As a result of being inundated with so much information that is not consistent or valid, we do not know which information is true and which is not. This causes us to feel unsure of ourselves (i.e., we are not able to trust our judgement), and it fosters a sense of morally helplessness.